SIMULATING MANY-BODY SYSTEMS
June 18, 2018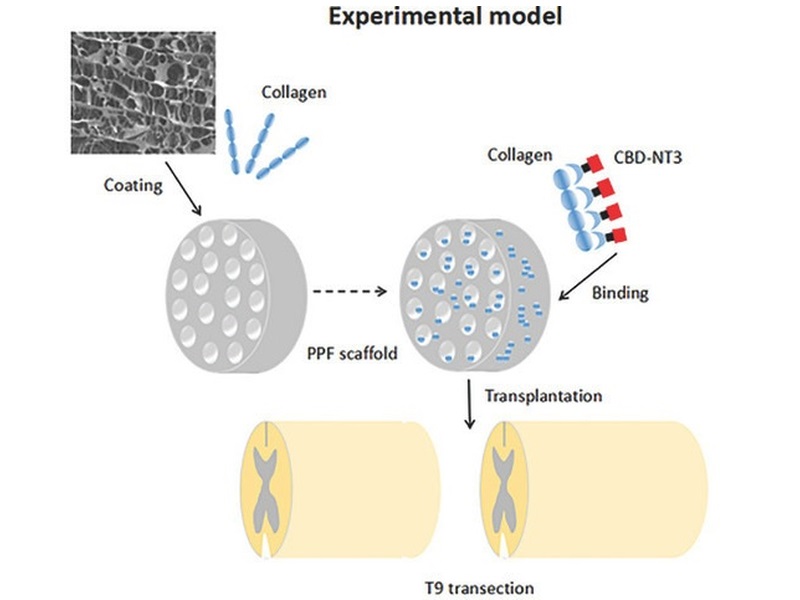
Combinatorial treatment consisting of 3D printed multichannel biodegradable scaffolds and collagene loaded with Nerve Growth Factor facilitates axonal and neuronal regeneration
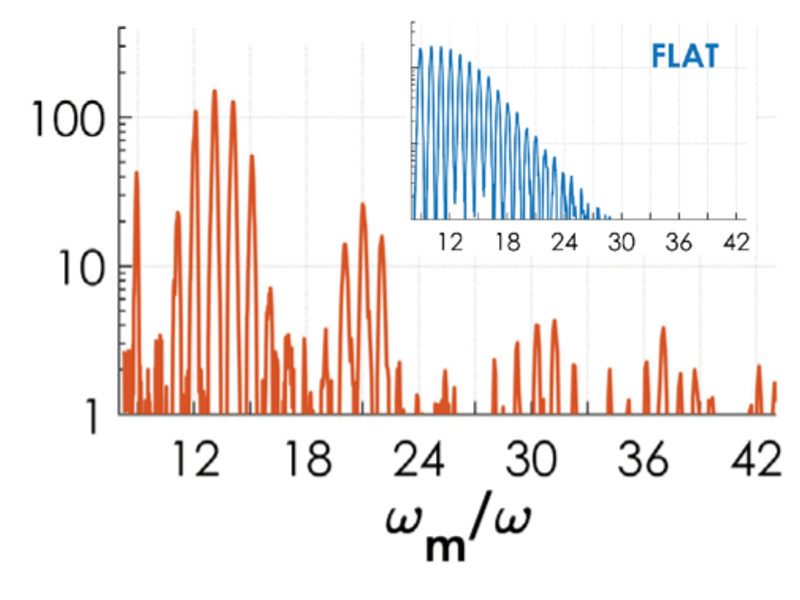
July 9, 2018A way to produce spatially separated attosecond pulses of coherent extreme ultraviolet (XUV) radiation is to irradiate a solid grating by a superintense, femtosecond laser pulse. By simultaneously allowing for surface plasmon excitation and optimizing the electron density profile on a sub-micrometer scale, Giada Cantono and coworkers obtained a strong enhancement of XUV emission in the grazing direction. Analysis of the experimental data with the aid of simulations shows that the XUV emission is boosted by nanobunching of the relativistic electrons which are accelerated by the surface plasmons and scatter the laser field, analogously to what happens in a free electron laser. Besides possible applications of the XUV emission, which is quasi-collinear to high charge electron bunches, the results demonstrate improved control of “extreme” plasmonics at high field intensities and ultrashort durations. The research is published in Physical Review Letters.
G. Cantono, L. Fedeli, A. Sgattoni, A. Denoeud, L. Chopineau, F. Réau, T. Ceccotti, and A. Macchi
Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 264803 (2018), https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.264803